WHAT IS RADAR?
RADAR stands for Radio Detection & Ranging
It is basically a system used to detect the reflecting object such as aircraft, ships, spacecraft, vehicles, people & the natural environment.
BASIC PRINCIPLE OF RADAR SYSTEM
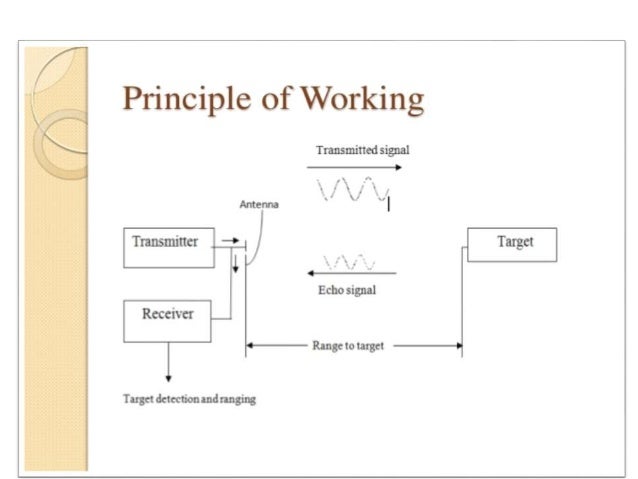
FIG. BASIC PRINCIPLE OF RADAR
RADAR is an object.
The transmitter in RADAR generates electromagnetic waves to determine the range, Angle, Distance & Velocity of the target.
The transmitter generates an electromagnetic wave & radiated through the antenna toward the target through free space. These electromagnetic waves reflected again from the target in a form of an echo signal.
These echo signals are received through an antenna. Based on the echo signal, RADAR can measure Range, Distance, Velocity & Angle of Target.
The doppler frequency shift is widely used in radar for separating the moving target from the fixed target.
Echo signal receives from the fixed target such as Land, Sea, Rain is called Clutter. Clutter is the unwanted signal.
ADVANTAGES OF RADAR
1. RADAR can identify unknown objects through Darkness, Rain, Fog, Snow.
2. RADAR can identify the Range, Distance, Angle, Position & Velocity of the target based on the Echo signal.
LIMITATION
1.RADAR can not be used for short distances.
2.RADAR can not identify the colour of the target.
APPLICATION
It is used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather terminology.
BISTATIC RADAR

FIG. BISTATIC RADAR
The RADAR system consists of a transmitting antenna which is connected to the transmitter & an antenna is connected to the receiver. such a RADAR system is called a BISTATIC RADAR.
The transmitter radiates an electromagnetic wave generated by the oscillator. A portion of the wave reflected back from the target in a form of an Echo signal in all directed toward the receiver.
The receiver antenna collects the returned Echo signal & deliver it to the receiver. The receiver detects the target & its relative velocity. which respect to the Radar station. If the target is moving.
MONOSTATIC RADAR

FIG. MONOSTATIC RADAR
A single antenna is used for both transmitting & Receiving signals in a RADAR is called a Monostatic RADAR.
RADAR consists of a transmitter, a receiver, a display & an antenna.
The function of the Duplexer is:
1.To separate the transmitter & receiver during transmission & reception.
2.To protect the receiver from high power transmitter.
3.It uses a single transmitter/receiver antenna.
It is possible to detect the height, speed & direction of the target & time taken for the Echo to come back after reflection from the target.
The display screen indicates the target data.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE MAXIMUM RANGE OF RADAR:
(A) TRANSMITTER POWER:
In case the Radar range is to be doubled, we have to increase the transmitter power 16 times.
If Rmax↑=2Rmax
Then Pt↑=16 Pt
since Rmax ∝ Pt to the power¼
(B) FREQUENCY :
The increase in frequency increase in Range
Rmax ∝ √for Rmax ∝ 1\√λ
then √f = 1\√λ